New nuclear medicine facility boosts private medical care in Limpopo
Drickus Maartens • March 4, 2020
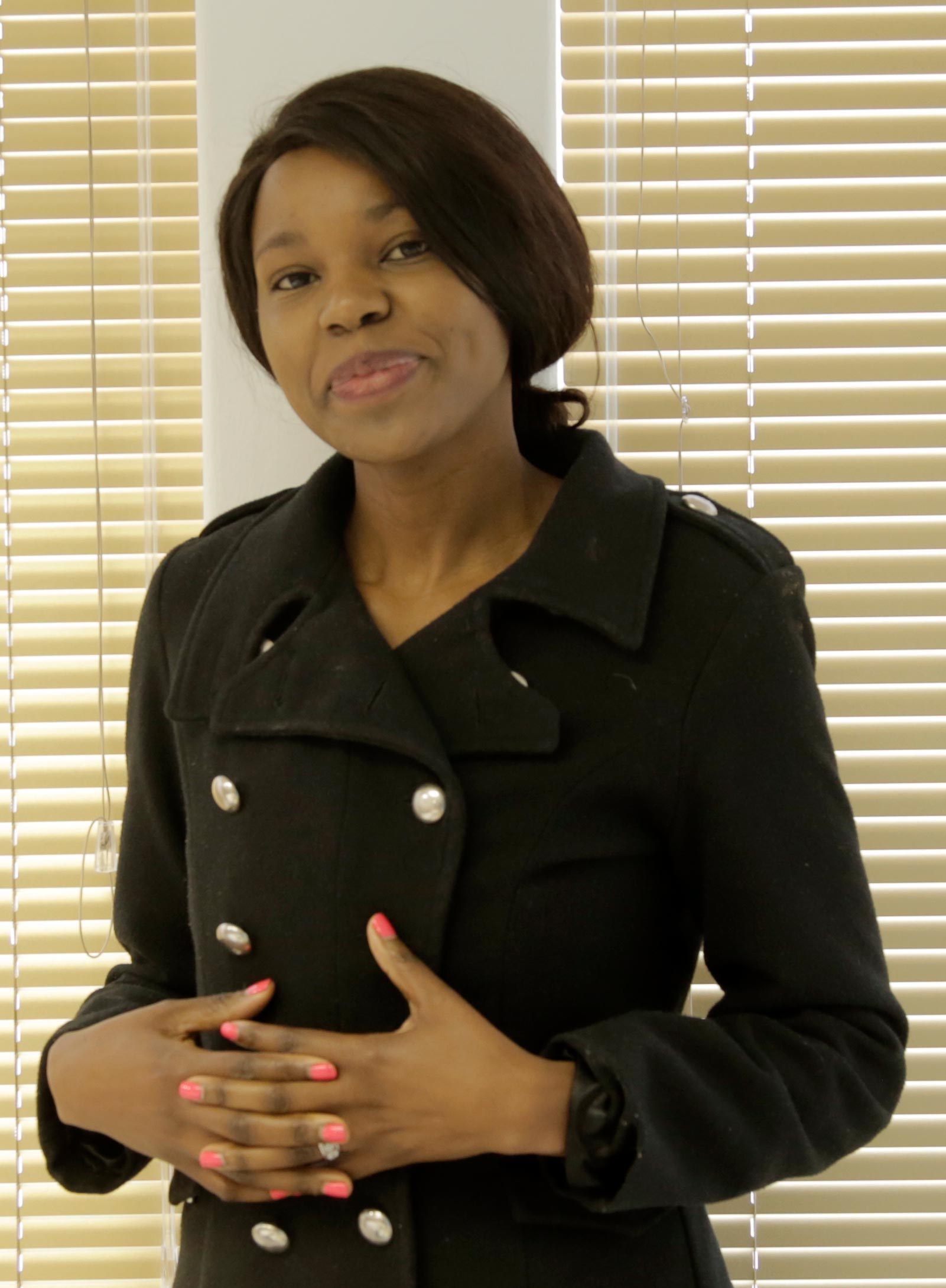
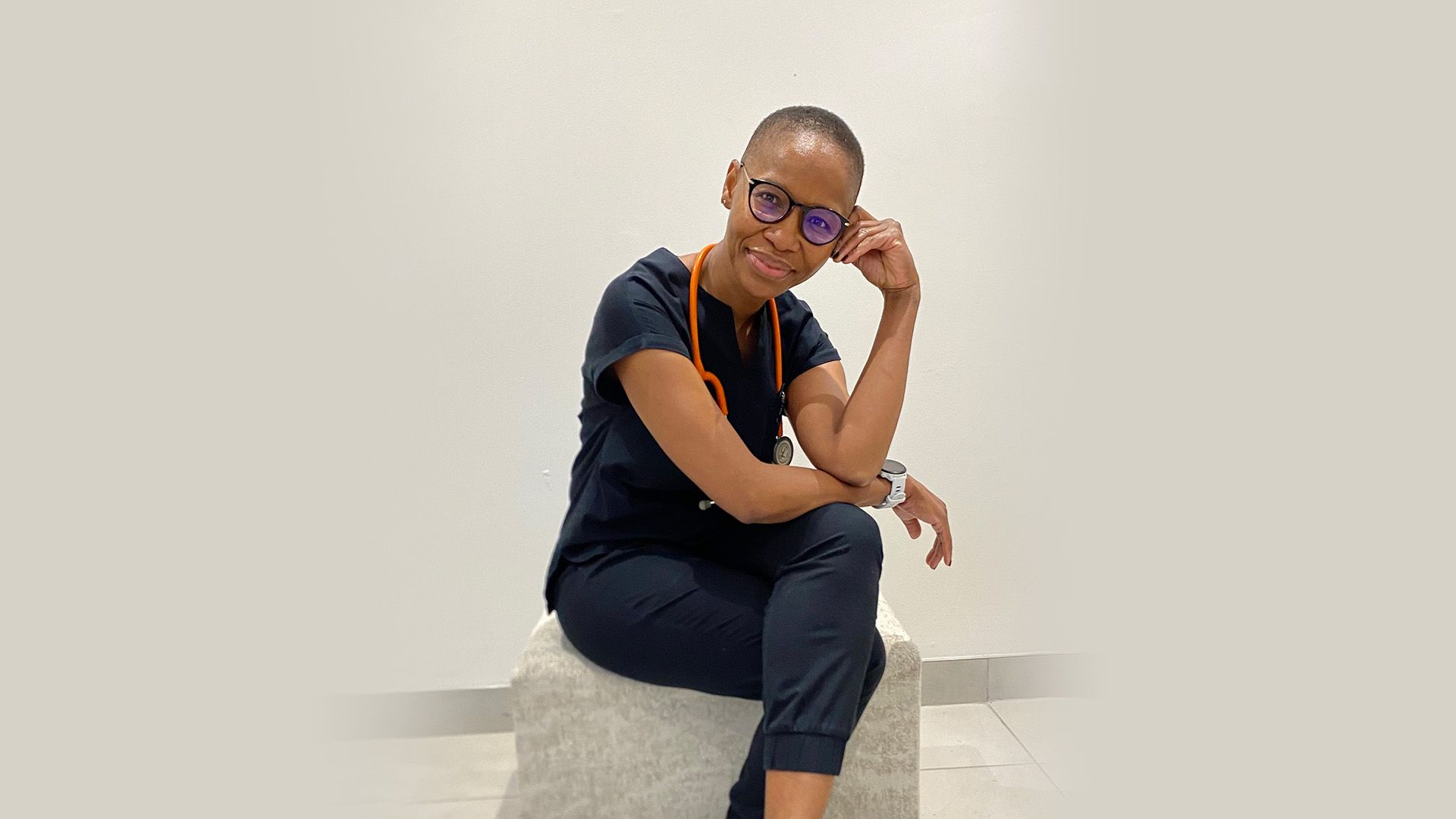
Dr Ntanganedzeni Muambadzi, the only nuclear medicine specialist based permanently in Limpopo, is committed to develop this important field of medicine to serve the people of the province.
Super specialist contributes to the advancement of medicine in province
Dr Ntanganedzeni Muambadzi — the only nuclear medicine specialist based permanently in Limpopo province — is a woman with a vision to develop this important field of medicine to serve the people of the province.
“There has been a lack of critical nuclear medicine services for the province’s population of some 5.4 million people, which has resulted in many of them not having had access locally to the diagnostic investigations and treatments that they needed,” comments Dr Muambadzi, who is acting head of the nuclear medicine department at Polokwane Provincial Hospital and who has recently also established a part-time private practice at Netcare Pholoso Hospital.
“I grew up in Vhembe district and studied in Gauteng, and returned to the province of my birth in 2017 with the express intention of filling the gap that existed locally in this important area of medicine. It is such a wonderful privilege to have the opportunity to develop dedicated nuclear medicine services within both the public and private sectors, and to be able to serve the most vulnerable within the communities of my home province,” says Dr Muambadzi.
Explaining the role of nuclear medicine, Dr Muambadzi says that nuclear materials are used in many medical technologies and treatments, and that nuclear medicine procedures enable medical practitioners to obtain key health information about a patient’s condition that may otherwise require more invasive diagnostic tests or surgery.
“First developed in the 1950s, nuclear medicine essentially involves the use of small amounts of radioactive material for the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of diseases. These include different types of cancers, heart diseases, gastrointestinal conditions, neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and many others. Furthermore nuclear medicine is also used for research.”
Dr Muambadzi says that although nuclear medicine has many applications, it is particularly well-known and important in the detection and ongoing monitoring and treatment of various types of cancers. It is particularly effective for identifying cancers at their earliest stages, when cancers tend to be most responsive to treatment.
“Nuclear medicine is also used to target cancer treatment more precisely and to establish how well a patient is responding to treatment,” says Dr Muambadzi, who is also a member of the Breast Cancer Steering Committee of the Polokwane/Mankweng Hospital Complex (PMHC) and has been recognised with the Board of Healthcare Funders (BHF) Titanium Young Doctors Achiever Award for 2017/18.
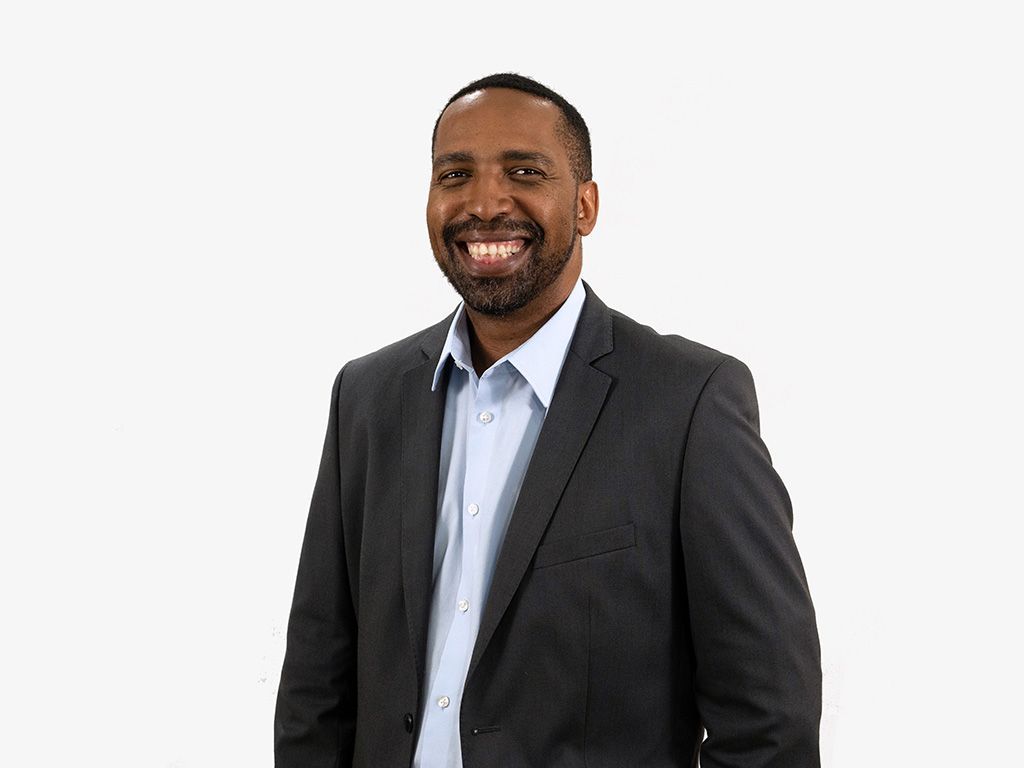
“Since her return to the province three years ago, Dr Muambadzi has contributed immensely to the development of nuclear medicine to the benefit of the local population and her medical colleagues. In addition to developing dedicated nuclear medicine departments in the public and private hospitals, she is also actively involved in education, lecturing radiology registrars who are training in specialist or sub-specialist fields at Mankweng Hospital, and is a member of the University of Limpopo’s School of Medicine Board,” says Netcare Pholoso Hospital’s general manager, Fabion Bennett.
Bennett adds that, in partnership with the hospital, Dr Muambadzi has developed a dedicated nuclear medicine facility — the first of its kind in the private sector in Limpopo province — which commenced operations in mid-February 2020. “We are most grateful to have a nuclear specialist of Dr Muambadzi’s calibre providing this important medical service to patients at our hospital.”
Bennett points out that Limpopo Health MEC, Dr Phophi Ramathuba, announced during her 2017 budget speech, that the department would start attracting and recruiting ‘super’ specialists to the Mankweng Hospital complex and the new medical school at the University of Limpopo. The aim of this was to be in a position to provide medical services within Limpopo that are of sufficiently high standard to ensure that patients do not have to be referred to other centres in South Africa to get the specialist medical care they need.
“Netcare and Netcare Pholoso Hospital are proud to be collaborating with the Limpopo Health Department in an initiative to provide the necessary opportunities to attract and retain outstanding young specialists to the province,” he says.
“What is most pleasing about this collaboration is that together we are succeeding in attracting many gifted and dedicated young specialists back to the province of their birth once they have completed all of their speciality and sub-speciality training. A number of them, including Dr Muambadzi, have already made an immense contribution to the advancement of medicine within our region,” concludes Bennett.
Dr Muambadzi’s contact details
Consulting rooms: 48 Grobler Street (Cnr Plein), Polokwane
Tel 015 230 0128 or 065 902 8215
Consulting hours: 07:00 – 17:00
24-hour service